Have you ever wondered how your video calls stay crystal clear or how vast amounts of data travel across the globe in an instant? The answer lies in optical fiber communication, a revolutionary approach that uses fiber optic cables to transmit information as light signals. This cornerstone of fiber optic technology has transformed how we connect, offering speed and reliability like never before. In this beginner-friendly guide, we’ll dive into what optical fiber communication is, how it works, its benefits, and its role in our daily lives. We’ll keep it simple and engaging, so you can appreciate the magic behind this technology. With solutions from CommMesh, let’s explore the world of optical fiber communication and its impact on data transmission!
What Is Optical Fiber Communication?
Defining Optical Fiber Communication
Optical fiber communication is a method of transmitting information using light pulses through fiber optic cables. These cables, made of thin strands of glass or plastic, carry data transmission over long distances with minimal loss. Unlike traditional copper wires that use electrical signals, optical fiber communication relies on light, making it a key innovation in fiber optic technology for modern telecommunications.

The Evolution of Optical Fiber Communication
Optical fiber communication has evolved significantly since its early days in the 1960s, when researchers first explored using light for data transmission. Early systems faced challenges with signal loss, but advancements in fiber design and laser technology have made optical fiber communication a global standard in fiber optic technology, powering everything from internet networks to undersea cables.
Principles of Optical Fiber Communication
Light Propagation in Fiber Optic Cables
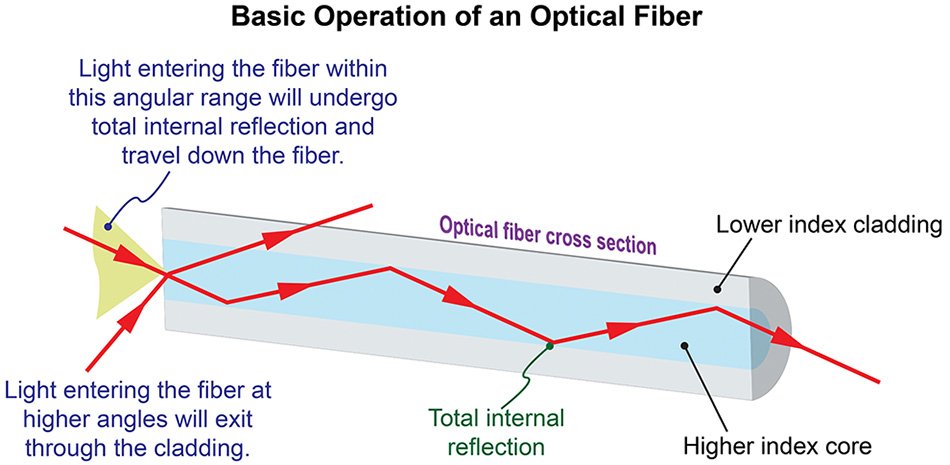
Optical fiber communication works by sending light signals through fiber optic cables, which consist of a core and cladding. The core, where light travels, is surrounded by a cladding layer with a lower refractive index, causing total internal reflection. This principle in fiber optic technology ensures light stays within the cable, enabling efficient data transmission over long distances.
Modulation and Demodulation
In optical fiber communication, data transmission is achieved by modulating light signals—turning them on and off to represent binary data (1s and 0s). At the receiving end, demodulation converts these light pulses back into electrical signals. This process in fiber optic technology ensures accurate and rapid communication across fiber optic cables.
Signal Attenuation and Dispersion
Signal attenuation and dispersion are key considerations in optical fiber communication. Attenuation refers to the loss of light intensity over distance, while dispersion causes light pulses to spread, potentially blurring data transmission. Advances in fiber optic technology have reduced these effects, making optical fiber communication more reliable for global networks.
Components of Optical Fiber Communication
Fiber Optic Cables
The heart of optical fiber communication is the fiber optic cables, which come in single mode and multimode varieties. Single mode cables, with a smaller core, are used for long-distance data transmission, while multimode cables suit shorter distances with higher bandwidth. These cables are essential in fiber optic technology for carrying light signals.
Transmitters and Receivers
Transmitters in optical fiber communication convert electrical signals into light pulses using lasers or LEDs, sending data transmission through fiber optic cables. Receivers then convert these light signals back into electrical data. This duo drives fiber optic technology, ensuring seamless communication across networks.
Connectors and Splices
Connectors and splices link fiber optic cables in optical fiber communication, maintaining signal integrity during data transmission. Connectors like LC or SC allow easy attachment, while splices fuse fibers for permanent joins. These components in fiber optic technology ensure efficient and reliable network setups.

Advantages of Optical Fiber Communication
High Bandwidth and Speed
One major advantage of optical fiber communication is its high bandwidth, supporting massive data transmission rates. Light signals travel faster than electrical signals, making fiber optic cables ideal for fiber optic technology in applications like 5G networks and streaming services, where speed is critical.
Long-Distance Capability
Optical fiber communication excels at long-distance data transmission due to low signal loss. Unlike copper cables, fiber optic cables can carry data across continents or under oceans with minimal repeaters, a key strength in fiber optic technology for global telecommunications.
Immunity to Electromagnetic Interference
Fiber optic cables in optical fiber communication are immune to electromagnetic interference, unlike copper wires affected by electrical noise. This makes optical fiber communication reliable in fiber optic technology for environments with heavy machinery or electrical equipment, ensuring consistent data transmission.
Applications of Optical Fiber Communication

Telecommunications
Optical fiber communication powers telecommunications, providing the backbone for phone calls, internet, and TV services. Fiber optic cables enable high-speed data transmission across cities and countries, making optical fiber communication a cornerstone of fiber optic technology in connecting the world.
Data Centers and Internet Infrastructure
Data centers rely on optical fiber communication for fast data transmission between servers and storage systems. The high density of fiber optic cables in these facilities supports fiber optic technology, ensuring efficient operations for cloud computing and online services.
Medical and Industrial Uses
In medical fields, optical fiber communication supports imaging devices and remote diagnostics, using fiber optic cables for precise data transmission. Industrially, it enables automation and monitoring systems, showcasing fiber optic technology’s versatility in specialized applications.
Challenges of Optical Fiber Communication
High Installation Costs
One challenge of optical fiber communication is its high initial cost. Installing fiber optic cables requires specialized equipment and labor, making it a significant investment in fiber optic technology. However, the long-term benefits often justify the expense for data transmission needs.
Fragility of Fiber Optic Cables
Fiber optic cables can be fragile compared to copper wires, requiring careful handling during installation. This fragility in optical fiber communication poses a challenge in fiber optic technology, necessitating protective measures to ensure reliable data transmission.
Maintenance and Repair Complexity
Repairing fiber optic cables in optical fiber communication is complex, often requiring skilled technicians to splice fibers accurately. This maintenance challenge in fiber optic technology can lead to downtime, affecting data transmission until repairs are completed.
Optical Fiber Communication vs Traditional Methods
Comparison with Copper Cables
Optical fiber communication outpaces traditional copper cables in speed and bandwidth for data transmission. While copper is cheaper and easier to install, fiber optic cables offer superior performance in fiber optic technology, making optical fiber communication the preferred choice for modern networks.

Reliability and Distance
In terms of reliability and distance, optical fiber communication surpasses copper due to lower signal loss over long distances. This advantage in fiber optic technology makes fiber optic cables ideal for data transmission across vast regions, unlike copper’s limitations.
Cost and Infrastructure Needs
Copper cables have lower upfront costs than optical fiber communication, but fiber optic cables require more infrastructure investment. Over time, the durability and efficiency of optical fiber communication in fiber optic technology offset these costs for high-demand data transmission applications.
Comparison Table: Optical Fiber vs Copper
To make the differences clearer, here’s a simple table comparing optical fiber communication and copper cables:
| Aspect | Optical Fiber | Copper Cable |
|---|---|---|
| Speed | High, supports 5G | Lower, limited bandwidth |
| Distance | Long, minimal loss | Short, significant loss |
| Interference | Immune to EMI | Susceptible to EMI |
| Cost | Higher initial cost | Lower initial cost |
| Durability | Fragile, needs care | More robust |
This table shows why optical fiber communication is increasingly favored in fiber optic technology for advanced data transmission, despite copper’s initial cost advantage.
Choosing Optical Fiber Communication for Your Needs
Assessing Bandwidth Requirements
When considering optical fiber communication, evaluate your bandwidth needs—high-speed applications like video streaming benefit from fiber optic cables. This ensures optical fiber communication in fiber optic technology meets your data transmission demands effectively.
Evaluating Distance and Environment
Choose optical fiber communication for long-distance or interference-prone environments where fiber optic cables outperform copper. This decision in fiber optic technology ensures reliable data transmission across diverse settings, from urban to rural areas.
Balancing Cost and Long-Term Benefits
While optical fiber communication has higher upfront costs, its long-term benefits in data transmission often outweigh the expense. Weigh these factors in fiber optic technology to determine if fiber optic cables are the right fit for your infrastructure.

Future Trends in Optical Fiber Communication
Advances in Fiber Design
Future optical fiber communication will benefit from improved fiber optic cables, such as bend-insensitive fibers. These advancements in fiber optic technology will enhance data transmission efficiency, making installation easier and performance better.
Integration with 5G and Beyond
As 5G and future networks emerge, optical fiber communication will play a vital role in supporting high-speed data transmission. Fiber optic cables will underpin the backbone of these networks, driving fiber optic technology into new frontiers of connectivity.
Expansion into Smart Cities
Optical fiber communication is set to expand into smart city projects, enabling data transmission for IoT devices and infrastructure monitoring. This growth in fiber optic technology will make fiber optic cables essential for urban development and sustainability.
Conclusion: The Power of Optical Fiber Communication
Optical fiber communication is like the superhighway of the digital age, carrying data transmission at lightning speed across fiber optic cables. We’ve explored what optical fiber communication is, how it works, its advantages, and its future in fiber optic technology, showing its transformative impact on our connected world. Whether it’s powering your internet, supporting medical innovations, or building smart cities, optical fiber communication keeps us linked with unmatched reliability. With solutions from CommMesh, you can harness fiber optic technology to stay ahead—embrace the light and stay connected!

