The fiber optic cable core is the fundamental material at the heart of fiber optic cables, enabling the transmission of light signals for high-speed data communication in fiber optic technology. As the primary component that carries light within a fiber optic cable, the fiber optic cable core is a crucial material used in the manufacturing of these cables, which power everything from global internet networks to local broadband systems. This beginner-friendly guide will explore what a fiber optic cable core is, its composition, types, benefits as a material, challenges in its production, its role in fiber optic cable manufacturing, and future trends in its development. Whether you’re new to fiber optic technology or seeking to understand the materials behind fiber optic cables, this article will highlight the fiber optic cable core’s pivotal role in modern connectivity.

What Is a Fiber Optic Cable Core?
Defining Fiber Optic Cable Core
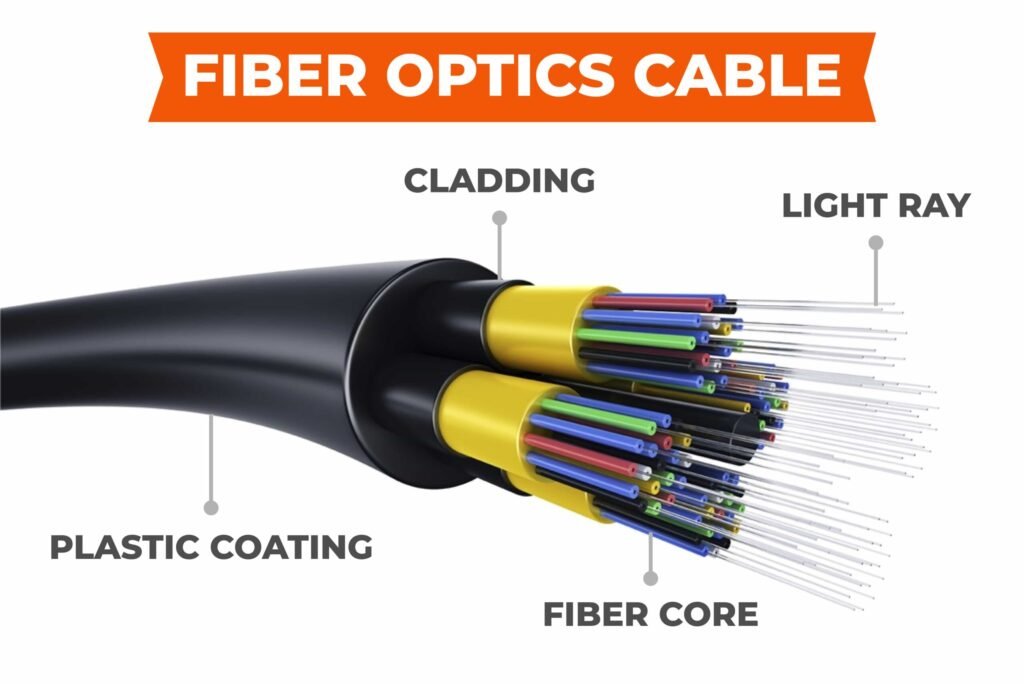
The fiber optic cable core is the central material within a fiber optic cable responsible for transmitting light signals to carry data. In fiber optic technology, the fiber optic cable core consists of thin strands of glass or plastic, typically 8 to 62.5 microns in diameter, surrounded by a cladding layer that ensures light remains within the core through total internal reflection. This material is the foundation of fiber optic cables, distinguishing them from copper cables by using light instead of electricity. The fiber optic cable core is a critical material in the production of fiber optic cables, enabling their use in various applications within fiber optic technology.
Composition of Fiber Optic Cable Core
The fiber optic cable core is made from high-purity materials designed to optimize light transmission. In fiber optic technology, the primary material for the fiber optic cable core is ultra-pure silica glass, which offers low signal loss and high clarity. For shorter-range or cost-sensitive applications, plastic such as polymethyl methacrylate (PMMA) is used to create the fiber optic cable core. The core is surrounded by a cladding layer, typically made of silica glass doped with fluorine or boron to lower its refractive index, ensuring efficient light reflection. A protective coating, often acrylate or silicone, is applied to the fiber optic cable core to shield it from moisture and scratches, making it a durable material for fiber optic cables in fiber optic technology.
Types of Fiber Optic Cable Core Materials
The fiber optic cable core varies in type based on its intended use in fiber optic cables. In fiber optic technology, there are two main types: single-mode and multimode fiber optic cable cores. Single-mode fiber optic cable cores have a small diameter (8-10 microns) and are made of silica glass, designed for long-distance transmission with a single light path. Multimode fiber optic cable cores, with a larger diameter (50 or 62.5 microns), can be made of silica glass or plastic, supporting multiple light paths for shorter distances. These material types influence the performance of fiber optic cables, making the fiber optic cable core a versatile material in fiber optic technology.

Benefits of Fiber Optic Cable Core as a Material
Exceptional Light Transmission Efficiency
The fiber optic cable core offers exceptional light transmission efficiency as a material in fiber optic technology. Made from ultra-pure silica glass or plastic, the fiber optic cable core minimizes signal loss through its low attenuation properties, allowing light to travel long distances with clarity. This efficiency ensures that fiber optic cables manufactured with a fiber optic cable core can achieve high-speed data transmission, such as 100 Gbps or more. The fiber optic cable core’s ability to maintain light signal integrity makes it a superior material for producing high-performance fiber optic cables in fiber optic technology.
Compatibility with Diverse Cable Designs
The fiber optic cable core is highly compatible with various fiber optic cable designs, enhancing its utility as a material. In fiber optic technology, the fiber optic cable core can be integrated into loose tube fiber optic cables (up to 24 cores) or tight buffer fiber optic cables (144 cores or more), depending on the application. Its versatility—whether as a single-mode or multimode fiber optic cable core—allows manufacturers to tailor fiber optic cables for specific needs, such as outdoor long-haul networks or indoor high-density setups. This adaptability makes the fiber optic cable core an essential material in fiber optic technology.
Durability Under Protective Layers
Despite its delicate nature, the fiber optic cable core offers durability when properly protected, making it a reliable material. In fiber optic technology, the fiber optic cable core is coated with acrylate or silicone during manufacturing, safeguarding it against moisture, scratches, and minor impacts. When integrated into fiber optic cables with additional layers like aramid yarn and outer jackets, the fiber optic cable core withstands environmental stresses, such as temperature changes or mechanical strain. This durability ensures that the fiber optic cable core remains a dependable material for producing long-lasting fiber optic cables in fiber optic technology.
Challenges of Fiber Optic Cable Core as a Material
High Precision Required in Manufacturing
Producing the fiber optic cable core as a material requires high precision, presenting a challenge in fiber optic technology. The fiber optic cable core must be made from ultra-pure silica or plastic, free of impurities that could disrupt light transmission. The manufacturing process involves drawing the fiber optic cable core into precise diameters (e.g., 8 microns for single-mode), requiring advanced equipment and strict quality control. Any defects in the fiber optic cable core can impair the performance of fiber optic cables, making its production a complex and costly aspect of fiber optic technology.
Fragility During Handling and Processing
The fiber optic cable core is fragile as a material, complicating its handling and processing. In fiber optic technology, the glass or plastic composition of the fiber optic cable core makes it prone to cracking if bent too sharply or mishandled during manufacturing or cable assembly. This fragility requires careful processing when integrating the fiber optic cable core into fiber optic cables, often necessitating specialized tools and skilled technicians. The delicate nature of the fiber optic cable core poses a challenge for manufacturers in fiber optic technology, impacting production efficiency.
Cost of High-Quality Raw Materials
The cost of raw materials for the fiber optic cable core can be high, affecting its use in fiber optic technology. Ultra-pure silica glass, the primary material for the fiber optic cable core, requires significant refinement to achieve the necessary clarity, driving up production costs. Even plastic fiber optic cable cores, while cheaper, need high-quality polymers to ensure performance in fiber optic cables. These material costs can make the fiber optic cable core an expensive component in fiber optic technology, particularly for large-scale cable manufacturing projects.
Applications of Fiber Optic Cable Core in Cable Manufacturing
Use in Loose Tube Fiber Optic Cables
The fiber optic cable core is a key material in manufacturing loose tube fiber optic cables. In fiber optic technology, loose tube fiber optic cables typically contain up to 24 fiber optic cable cores, housed in gel-filled tubes to protect against moisture and temperature changes. The fiber optic cable core in these cables, often single-mode for long-distance transmission, is used to create robust outdoor cables for telecommunications and undersea networks. This application highlights the fiber optic cable core’s role as a material in producing durable fiber optic cables in fiber optic technology.
Use in Tight Buffer Fiber Optic Cables
In tight buffer fiber optic cables, the fiber optic cable core enables high-density configurations. In fiber optic technology, tight buffer fiber optic cables can incorporate 144 fiber optic cable cores or more, with each core individually buffered for strength and flexibility. These cables, often using multimode fiber optic cable cores, are manufactured for indoor applications like data centers and LANs, where high bandwidth is critical. The fiber optic cable core’s adaptability as a material ensures that fiber optic cables meet the demands of dense connectivity in fiber optic technology.
Use in Specialty Fiber Optic Cables
The fiber optic cable core is also used in manufacturing specialty fiber optic cables for niche applications. In fiber optic technology, specialty cables—such as those for medical endoscopes or industrial sensors—rely on the fiber optic cable core for precise light transmission. These cables may use a single fiber optic cable core or a small bundle, tailored for flexibility and clarity, often in harsh environments. This application demonstrates the fiber optic cable core’s versatility as a material in creating specialized fiber optic cables in fiber optic technology.
Future Trends in Fiber Optic Cable Core Development
Advancements in Material Purity and Performance
Future developments in the fiber optic cable core will focus on enhancing material purity and performance. In fiber optic technology, researchers are working on even purer silica glass for the fiber optic cable core to reduce signal loss further, enabling faster and longer-distance transmission in fiber optic cables. Advanced plastic fiber optic cable cores with improved clarity are also being explored for cost-effective applications. These advancements will elevate the fiber optic cable core’s role as a material in fiber optic technology.
Development of Flexible and Bend-Resistant Cores
The fiber optic cable core will see improvements in flexibility and bend resistance. In fiber optic technology, new glass compositions and polymer coatings are being developed to make the fiber optic cable core less prone to cracking, even under tight bends. This will simplify the manufacturing of fiber optic cables for complex installations, such as in urban wiring or flexible devices, enhancing the fiber optic cable core’s utility as a material in fiber optic technology.
Integration with Emerging Technologies
The fiber optic cable core will integrate with emerging technologies like quantum communication. In fiber optic technology, the fiber optic cable core’s low-loss properties make it ideal for transmitting quantum states of light, supporting ultra-secure networks. Innovations in the fiber optic cable core’s material structure, such as hollow-core designs, will further enhance its compatibility with future fiber optic cables, positioning it as a key material in advancing fiber optic technology.
Comparison Table: Glass vs Plastic Fiber Optic Cable Core
To highlight differences, here’s a comparison of glass and plastic fiber optic cable cores as materials:
| Aspect | Glass Fiber Optic Cable Core | Plastic Fiber Optic Cable Core |
|---|---|---|
| Material | Ultra-pure silica glass | Polymethyl methacrylate (PMMA) |
| Transmission Distance | Up to 100 km | Up to 100 meters |
| Bandwidth | Higher, supports 100+ Gbps | Lower, up to 10 Gbps |
| Cost | Higher, due to purity | Lower, more cost-effective |
| Application | Long-haul, telecommunications | Short-range, cost-sensitive |
This table illustrates how the choice of fiber optic cable core material impacts fiber optic cables in fiber optic technology.
Conclusion: Fiber Optic Cable Core as a Foundational Material
The fiber optic cable core is the foundational material that powers the performance of fiber optic cables, enabling high-speed, reliable data transmission in fiber optic technology. Its composition of silica glass or plastic, versatility in types, and benefits like efficient light transmission and compatibility with various cable designs make the fiber optic cable core indispensable in cable manufacturing. Despite challenges such as high precision requirements, fragility, and material costs, the fiber optic cable core’s role—enhanced by future advancements in purity, flexibility, and emerging technologies—ensures its continued importance. As connectivity demands grow, the fiber optic cable core will remain a vital material in shaping the future of fiber optic technology.

