Fikirkan a sambungan kabel gentian optik sebagai jahitan lancar yang memastikan data mengalir melalui rangkaian yang halus—seperti fabrik penyambung tukang jahit induk dengan ketepatan. Sama ada membaiki kabel yang rosak atau memanjangkan sambungan gentian, penyambungan gentian optik memastikan isyarat cahaya bergerak tanpa gangguan merentasi jarak yang jauh atau ruang yang sempit. Panduan ini meneroka segala-galanya tentang sambungan kabel gentian optik—daripada sambatan gabungan gentian asas kepada cara menyambung kabel gentian langkah demi langkah—merangkumi alatan, teknik dan petua praktikal. Dengan penyelesaian seperti daripada CommMesh, anda akan melihat mengapa menguasai sambung kabel gentian optik adalah kunci kepada ketersambungan yang teguh. Mari kita rungkai seni dan sains teknik sambatan gentian dan mulakan!
Apakah Sambungan Kabel Gentian Optik?

A sambungan kabel gentian optik ialah proses penyambungan dua kabel gentian optik secara kekal untuk mencipta laluan cahaya yang berterusan—penting apabila kabel dipotong, rosak atau perlu dipanjangkan. Tidak seperti penyambung, yang membenarkan pautan sementara, a sambungan kabel gentian optik fius gentian untuk kehilangan isyarat yang minimum—cth, 0.1 dB lwn. 0.3 dB untuk penyambung—menjadikannya sesuai untuk tulang belakang telekom atau pembaikan pusat data. Dalam penyambungan gentian optik, dua kaedah utama mendominasi: sambatan gabungan gentian, yang mencairkan gentian bersama-sama, dan penyambungan mekanikal, yang menjajarkannya secara fizikal—masing-masing sesuai dengan keperluan yang berbeza.
Sambungan gabungan gentian—standard emas—menggunakan haba untuk mencampurkan hujung kaca, memastikan ketahanan dan kehilangan yang rendah—cth, pautan 50 km dengan sambungan 0.05 dB kekal dalam bajet 17 dB untuk 10G. Penyambungan mekanikal, walaupun lebih cepat, menggunakan lengan—cth, menambah kehilangan 0.2 dB—lebih baik untuk pembaikan sementara. Kefahaman apa itu sambatan kabel gentian optik menetapkan peringkat untuk memilih pendekatan yang betul—sama ada anda menyambungkan penurunan 1 km atau batang sejauh 100 km.
Mengapa Menggunakan Fiber Fusion Splice dalam Rangkaian?
Sambungan gabungan gentian menonjol dalam sambungan kabel gentian optik untuk ketepatan dan kekekalannya—ini sebabnya ia diutamakan. Ia meleburkan hujung gentian dengan arka elektrik—cth, pada 2000°C selama 0.5 saat—mencipta ikatan yang hampir sempurna dengan kehilangan serendah 0.02 dB—cth, pautan 20 km dengan lima sambungan kehilangan hanya 0.1 dB jumlah. Kebolehpercayaan ini sesuai dengan rangkaian jarak jauh—fikirkan larian telekom sejauh 150 km—di mana setiap desibel dikira—cth, kekal di bawah 30 dB jumlah kerugian untuk isyarat 100G.
Di luar kerugian yang rendah, sambatan gabungan gentian tahan cuaca—cth, penutupan berkadar IP68 melindungi sambatan dalam hujan atau habuk—tidak seperti sambatan mekanikal, yang mungkin beralih (kehilangan 0.3 dB dari semasa ke semasa). Untuk penyambungan gentian optik dalam persediaan kritikal—cth, tulang belakang 5 km hospital—ketahanan fusion mengurangkan penyelenggaraan—cth, bertahan 20+ tahun berbanding 5-10 mekanikal. Dalam sambung kabel gentian optik keputusan, gabungan memerintah untuk prestasi.

Alat untuk Menyambung Kabel Gentian Optik
Berkesan sambungan kabel gentian optik memerlukan gear yang betul—inilah yang anda perlukan.
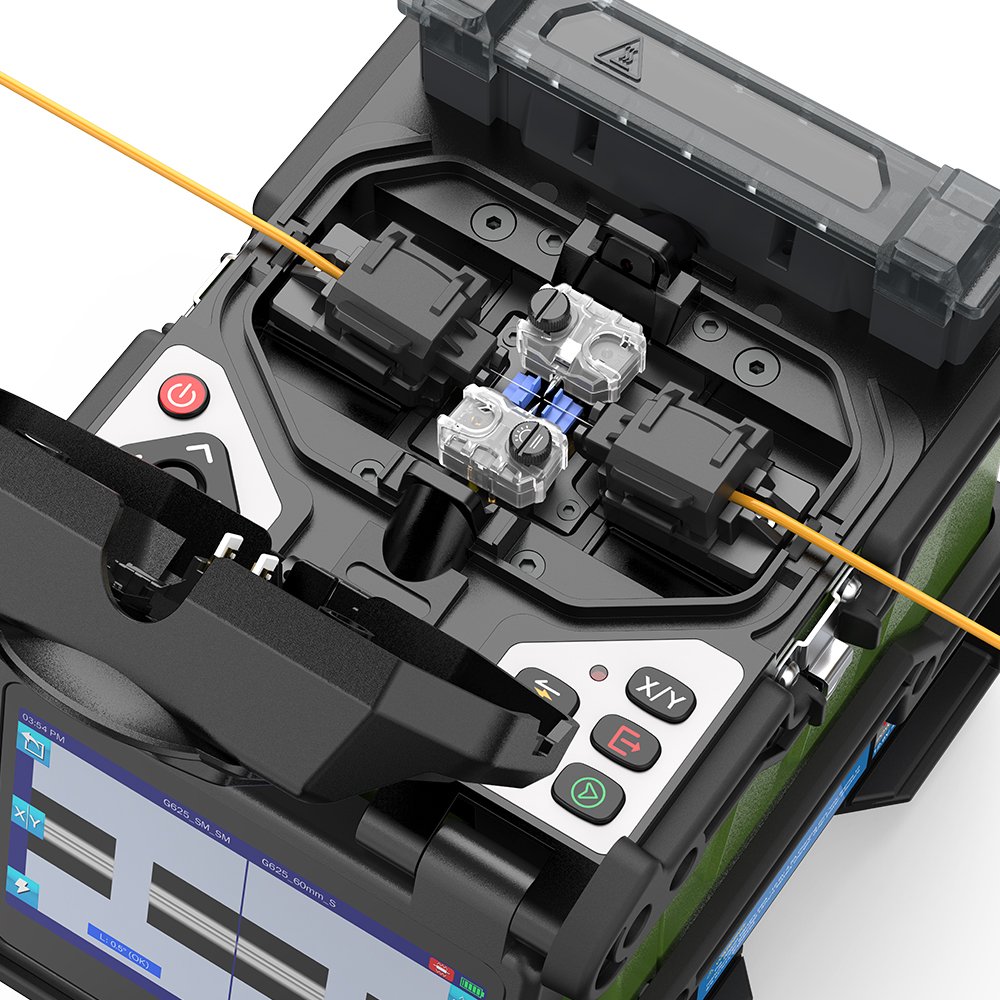
- Fusion Splicer: Hati daripada sambatan gabungan gentian—cth, unit $2000 menjajarkan dan mencairkan gentian dengan kehilangan <0.1 dB—penting untuk cara menyambung kabel gentian bersih—cth, larian 10 km dalam masa 10 minit.
- Pemangkas gentian: Memotong gentian rata—cth, pisau pemotong $500 memastikan sudut 0.5°—penting untuk kehilangan rendah teknik sambatan gentian—cth, menyediakan penurunan 1 km.
- Penanggal: Menanggalkan salutan—cth, jalur alat $50 mencantas jaket 250 μm—menyediakan gentian untuk penyambungan gentian optik—cth, mendedahkan kaca 125 μm.
- Lengan Sambatan: Melindungi sambatan—cth, tiub pengecutan haba $0.10 melindungi a sambatan gabungan gentian—digunakan dalam penutupan untuk sambung kabel gentian optik.
- OTDR: Mengesahkan sambung—cth, unit $5000 daripada CommMesh menyemak sambung 0.1 dB pada 5 km—kunci untuk sambungan kabel gentian optik kualiti.
Alat ini membuat cara menyambung kabel gentian tepat—CommMesh membekalkan semuanya.

Cara Menyambung Kabel Gentian: Langkah demi Langkah
Menguasai cara menyambung kabel gentian dengan a sambatan gabungan gentian mengikut proses yang jelas—ini panduannya.
Bersedia untuk Penyambungan Gentian Optik
- Jalur: Tanggalkan jaket—cth, 2 cm dari penimbal 900 μm—menggunakan penarik $50 untuk sambungan kabel gentian optik—mendedahkan teras 125 μm.
- Bersih: Lap dengan alkohol—cth, lap $5 buang habuk—pastikan bersih sambatan gabungan gentian—cth, mengelakkan kehilangan 0.2 dB daripada kotoran.
- belah: Potong pada 90°—cth, pisau pemotong $500 memotong gentian 50 μm—penting untuk sambung kabel gentian optik penjajaran—mengambil masa 5 minit untuk dua hujung.
Melakukan Sambungan Fiber Fusion
- Jajarkan: Muatkan gentian ke dalam penyambung—cth, teras penjajaran automatik unit $2000—penyediaan penyambungan gentian optik—cth, ketepatan 0.01 mm.
- Fius: Arka melebur berakhir—cth, 0.5 saat pada 2000°C—membentuk sambatan gabungan gentian—cth, kehilangan 0.05 dB pada pautan 10 km—mengambil masa 1-2 minit.
- Lindungi: Luncurkan lengan ke atas—cth, tiub $0.10 mengecut dalam 30 saat—mengamankan sambungan kabel gentian optik—jumlah masa 10-15 minit.
Uji dengan OTDR—cth, kehilangan 0.1 dB mengesahkan kejayaan—membuat cara menyambung kabel gentian boleh dipercayai.
Penyambung Mekanikal lwn. Penyambungan Fiber
Dalam sambungan kabel gentian optik, penyambungan mekanikal menawarkan alternatif kepada sambatan gabungan gentian. Ia menjajarkan gentian dalam lengan—cth, kit $5 dengan kehilangan 0.2 dB—tanpa lebur, sesuai dengan pembaikan pantas—cth, pembaikan kecemasan 500m dalam 5 minit—vs. gabungan 15 minit. Tiada penyambung diperlukan—hanya pisau pemotong dan penjalur—kos pemotongan—cth, $100 lwn. $2000 untuk teknik sambatan gentian.
Walau bagaimanapun, sambatan gabungan gentian menang untuk kekal—cth, kehilangan 0.05 dB lwn. 0.3 dB—dan kestabilan—cth, peralihan mekanikal dalam haba (0.5 dB sepanjang tahun). Untuk sambung kabel gentian optik dalam persediaan sementara—cth, pautan acara 1 km—kerja mekanikal; untuk jangka panjang—cth, 50 km telekom—paduan terbaik. Penyambungan gentian optik pilihan bergantung pada matlamat.
Cabaran dalam Penyambungan Kabel Gentian Optik
Sambungan kabel gentian optik menghadapi halangan—ini perkara yang perlu ditonton. Gentian kotor—cth, habuk menambah kehilangan 0.2 dB—memerlukan lap $5—cth, sambungan 5 km gagal pada 0.5 dB. Belah buruk—cth, sudut 2°—lompat kerugian kepada 0.3 dB—dibetulkan dengan pisau pemotong $500—penting untuk sambatan gabungan gentian. Cuaca—cth, -20°C mengeraskan kabel—melambatkan cara menyambung kabel gentian—cth, 20 minit lwn. 10 di dalam rumah.
Kos peralatan—cth, splicer $2000—mengerikan krew kecil—cth, kit mekanikal $500 menggoda—tetapi penyambungan gentian optik kualiti terjejas—cth, 0.4 dB lwn. 0.1 dB. Kepentingan kemahiran—cth, sambatan 0.5 dB orang baru berbanding latihan 0.05 dB seorang profesional ($500) membuahkan hasil. Sambungkan kabel gentian optik memerlukan penjagaan.
Kos dan Peralatan untuk Penyambungan Gentian Optik
Sambungan kabel gentian optik kos berbeza-beza—ini adalah ringkasannya. A sambatan gabungan gentian persediaan—penyambung ($2000), pisau pemotong ($500), penjalur ($50)—jumlah ~$2600—cth, penyambungan pautan 10 km dalam sehari—termasuk buruh $0.26/m. Kit mekanikal—$100—sesuai dengan kerja pantas—cth, pembaikan 500m untuk $50—tetapi sambung kabel gentian optik kerugian meningkat—0.3 dB lwn. 0.1 dB.
Kabel tambah—cth, $0.50/m untuk mod tunggal—$500 untuk 1 km—manakala lengan ($0.10) dan penutup ($20) melindungi penyambungan gentian optik—cth, $30 untuk larian 10-splice. CommMesh menawarkan alatan—cth, splicer $2000—mengimbangkan kos dan kualiti untuk sambatan gabungan gentian.
Kesimpulan: Menguasai Sambungan Kabel Gentian Optik
Sambungan kabel gentian optik mengikat rangkaian bersama-sama dengan kehalusan—sama ada melalui sambatan gabungan gentian atau cara mekanikal—seperti tukang menganyam jahitan yang sempurna. Panduan ini telah merangkumi semuanya—apa penyambungan gentian optik ialah, cara menyambung kabel gentian, dan mengapa alatan daripada CommMesh—bermula pada $50—membuatnya berfungsi. Dari 1 km FTTH jatuh ke batang 100 km, sambung kabel gentian optik dengan teknik sambatan gentian memastikan data mengalir. Cikgu sambungan kabel gentian optik hari ini dan bina hubungan yang berkekalan!

