In the ever-expanding world of telecommunications and power infrastructure, fiber optic cables have become indispensable for high-speed data transmission and reliable utility operations. As global fiber optic networks exceed 2 billion km in 2025 (per Địa lý viễn thám), overhead installations are increasingly favored for their cost-effectiveness and minimal disruption compared to underground burial. Two prominent types—ADSS (All-Dielectric Self-Supporting) cables and OPGW (Optical Ground Wire) cables—stand out for aerial deployments. At CommMesh, we specialize in premium fiber optic solutions, offering both ADSS and OPGW cables tailored for telecom operators, utility companies, and distributors. This guide provides a thorough comparison of ADSS and OPGW cables, covering structure, electrical functions, installation, environmental resistance, applications, and more, to help you choose the best fit for your project.
Introduction to ADSS and OPGW Cables
ADSS and OPGW cables are engineered for overhead use, utilizing existing utility poles or towers to deploy fiber optics without extensive trenching. Both support high-bandwidth data transmission, with capacities reaching 400 Gbps per channel via wavelength-division multiplexing (WDM), making them ideal for 5G backhaul, smart grids, and rural broadband. However, their designs differ fundamentally: ADSS is a fully non-metallic cable focused on simplicity and EMI immunity, while OPGW integrates metallic elements for dual-purpose grounding and communication.

The choice between ADSS and OPGW depends on environmental conditions, electrical requirements, and budget. ADSS is preferred for telecom-only setups due to its lightweight nature, while OPGW excels in power utility environments by serving as a ground wire. At CommMesh, our ADSS cables are designed for spans up to 1000 m with bend-insensitive fibers (5 mm radius, <0.01 dB loss), and OPGW options feature aluminum-clad steel for superior lightning protection (up to 100 kA fault current). Understanding these differences is key, as overhead cables reduce installation costs by 30–50% compared to underground alternatives, according to the Fiber Broadband Association.
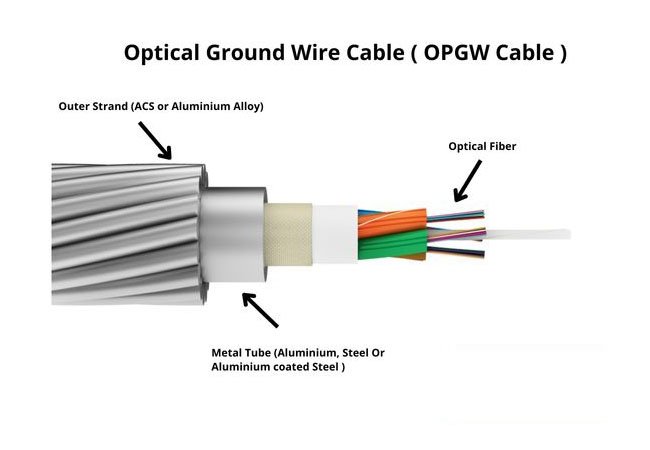
Structure and Material: Non-Metallic Simplicity vs. Metallic Durability
The structural composition of ADSS and OPGW cables is the foundation of their performance, influencing everything from weight to environmental resilience.
ADSS cables are completely non-metallic, eliminating any grounding needs. They use aramid yarn or glass fiber for strength, providing high tensile capacity (typically 1000–3000 N) without metal. The optical fibers—single-mode (9/125 μm) or multimode (50/125 μm)—are housed in loose tubes filled with water-blocking gel to prevent moisture ingress (IP68 rated, 0.1 MPa resistance). The outer jacket, usually polyethylene, offers UV protection and flexibility, making ADSS lightweight (100–200 kg/km) and easy to handle. This design avoids corrosion and EMI, ideal for areas near high-voltage lines (220–500 kV) where induced currents could cause 0.1 dB signal interference. However, without metal, ADSS relies on external supports for extreme loads.
In contrast, OPGW cables contain metallic components like steel, aluminum, or alloy cores, serving as both a communication medium and a ground wire. The fibers are protected in stainless steel tubes or central loose tubes, surrounded by aluminum alloy wires for reinforcement. This hybrid structure adds weight (200–400 kg/km) but enhances mechanical strength (up to 4000 N tensile) and electrical conductivity. The metallic core provides lightning protection and fault current discharge (50–100 kA), while the aluminum cladding resists corrosion in harsh climates. OPGW’s durability makes it suitable for power lines, but the metal increases installation complexity due to grounding requirements.
Overall, ADSS prioritizes lightweight flexibility for telecom-focused projects, while OPGW’s metallic durability suits utility integrations. At CommMesh, our ADSS cables feature advanced aramid reinforcement for 700 m spans without sagging, and OPGW variants include anti-corrosive grease for 30+ year lifespans in coastal areas. According to IEEE standards, non-metallic designs like ADSS reduce EMI risks by 100%, while metallic OPGW enhances grid reliability.
Electrical and Grounding Functions: EMI Immunity vs. Lightning Protection
Electrical properties are pivotal in overhead environments, where proximity to power lines poses risks.
ADSS cables are non-conductive, providing complete immunity to electromagnetic interference (EMI) and suitable for areas near power lines without grounding. This eliminates induced currents or outages during storms, ensuring signal integrity with attenuation below 0.2 dB/km even in high-EMI zones (e.g., 500 kV lines). However, without grounding, ADSS relies on dielectric materials to prevent arcing, making it ideal for telecom-only setups where electrical hazards are managed externally. The absence of metal also reduces theft risks in remote areas.
OPGW cables, on the other hand, are conductive and function as a ground wire, providing lightning protection and stable current discharge. They can handle short-circuit currents up to 100 kA, safeguarding the power grid while transmitting data. This dual role makes OPGW essential for high-voltage utilities, where it replaces traditional ground wires. However, installation requires power shutdowns to avoid shocks, and grounding is mandatory to prevent EMI (0.1 dB noise potential).
In summary, ADSS excels in EMI-free telecom applications, while OPGW offers integrated protection for utilities. CommMesh’s ADSS is optimized for 5G towers with zero EMI, and OPGW includes optical fibers in steel tubes for fault-tolerant grids.
Installation and Cost: Ease and Efficiency vs. Robust Security
Installation and cost are key decision factors, influencing project timelines and budgets.
ADSS cables are easy to install, requiring no power outage or grounding, with lightweight design allowing for longer spans (500–1000 m) and simpler hardware. Labor costs are lower (30–40% less than OPGW), with total project expenses at $0.80–$1.50/meter. This makes ADSS cost-effective for long spans in rural broadband or FTTx, where quick retrofits on existing poles save 20% on overall deployment. However, additional sag calculations are needed for wind/ice loads.
OPGW cables demand power shutdowns, grounding, and heavier equipment, increasing complexity and time by 20–50%. Costs range from $1.50–$3.00/meter due to metallic materials and safety protocols, but OPGW eliminates the need for separate ground wires, saving 15–20% long-term in utility projects. The higher initial investment is offset by reduced maintenance in high-risk areas.
CommMesh provides installation kits for both, with ADSS for rapid 5G rollouts (under 2 hours per span) and OPGW for secure utility upgrades, complying with Tiêu chuẩn IEC 60794 standards.
Environmental Resistance and Lifespan: Versatile Performance vs. Harsh-Environment Mastery
Environmental resilience determines cable longevity in overhead setups.
ADSS cables offer excellent resistance to electromagnetic fields, corrosion, wind, and ice, with flexible designs handling variable climates (-40°C to 70°C). Their non-metallic structure prevents rust, achieving a 20–25 year lifespan, though UV degradation may require jacket inspections every 5 years. ADSS is suited for diverse fields like FTTx and rural broadband, where lightweight construction minimizes ice load strain (up to 5 cm ice thickness).
OPGW cables provide strong resistance to high temperatures, harsh metals, and corrosion (via anti-corrosive grease), with superior performance in extreme environments. The metallic core extends lifespan to 25–35 years, but metal parts may corrode in salty air, requiring periodic checks. OPGW is best for power utilities (220–500 kV) and dual-use systems, enduring 100 mph winds and 10 cm ice loads.
Both types support 0.2 dB/km loss, but OPGW’s durability shines in storms. CommMesh’s ADSS uses UV-stabilized polyethylene for coastal use, and OPGW features galvanized steel for 40-year reliability.
Application Scenarios: Telecom Versatility vs. Utility Hybrid
Application fit is crucial for project success.
ADSS cables are ideal for cross-country telecom projects, FTTx, rural broadband, and diverse installations where EMI immunity is key. No power integration needed—perfect for telcos avoiding utility coordination, with spans up to 1000 m.
OPGW cables suit power + communication utilities (220–500 kV), stable dual-use systems where grounding is essential. They are optimal for high-voltage lines combining data transmission with grid protection, reducing overall infrastructure costs by 25%.
At CommMesh, ADSS excels in 5G access networks (no EMI), while OPGW powers smart grids with 10 Gbps overlay, per IEEE guidelines.
Weight and Flexibility: Lightweight Handling vs. Heavy-Duty Conductivity
Weight and flexibility affect logistics and performance.
ADSS cables are lightweight and easier to handle, with flexible designs for diverse installations like curved poles. Aramid yarn enables tight bends (10 mm radius) without loss, reducing shipping costs by 20%.
OPGW cables are heavier due to metallic components, less flexible but offering electrical conductivity over time, with robust stranding for long spans (500 m+). This makes them stable in wind but requires stronger supports.
CommMesh’s ADSS weighs 150 kg/km for easy aerial deployment, while OPGW at 300 kg/km provides 100 kA protection for utilities.
Case Studies: Real-World Deployments
- ADSS in Rural Broadband (India)
- BSNL’s 2025 5000 km project used ADSS (1.0 m aerial spans) for 100 Gbps 5G access, cutting costs by 35% with no grounding. Outcome: Connected 1 million homes with 99.9% uptime.
- OPGW in Smart Grid (U.S.)
- Duke Energy’s 3000 km upgrade in 2025 integrated OPGW on 500 kV lines for data and grounding, handling 80 kA faults. Outcome: Reduced outages by 25%, per utility reports.
Future Trends: Hybrid and Sustainable Designs
In 2025, trends favor hybrids combining ADSS flexibility with OPGW conductivity, using carbon fiber for 20% weight reduction. Sustainable materials (bio-jackets) and AI-optimized designs (dynamic load adjustment) will extend lifespans to 40 years.
Phần kết luận
ADSS and OPGW cables offer tailored solutions for Aerial fiber optics: ADSS for lightweight, EMI-immune telecom versatility, and OPGW for metallic, protective utility hybrids. With differences in structure, electrical functions, installation, and durability, your choice depends on project needs—ADSS for quick telecom installs, OPGW for robust power integration. As 5G and smart grids expand, both ensure future-proof networks. Explore CommMesh’s range at CommMesh for cables that deliver speed, safety, and sustainability.

